“AI is a brilliant tool for people to be more productive.”
Don’t take it from us. That’s Bill Gates speaking at Davos 2024.
As AI pervades industries across the globe, it’s already making headway in UX. Several new tools are popping up out of nowhere. Existing ones are adding AI capabilities to their product offerings. Recently, we examined the transformative impact of AI in user research.
However, some researchers and designers are still skeptical of AI use.
We understand their reservations. We’re here to convert the non-believers. AI will never replace human researchers and designers. Of that we’re convinced. It is also capable of augmenting our work so we can focus on deeper, more meaningful analysis.
We’ve scoured the web for the best UX AI tools for you to integrate into your workflow. Here’s what we’ll cover:
- Benefits & Limitations of AI in UX
- Where to Use AI in the UX Design Process
- Choosing the Right UX Tool with AI
- Top AI Tools to Augment UX Workflows
- Best Practices for Integrating AI into UX
Get ready for helpful tips, tricks and tools to elevate your research and design.


TL;DR – List of Top 8 UX AI Tools to Consider
AI for UX design promises to revolutionize the way that designers and researchers work. It generates greater efficiency and frees up a UX professional’s time for deeper analysis. In this article, we present eight of the best UX AI tools for different stages of the design process. We’ll dive into how each of the following tools leverage AI to improve the UX workflow from beginning to end:
- Marvin
- Qualtrics
- QoQo
- ChatGPT
- Uizard
- Adobe Sensei
- VisualEyes
- Attention Insight
ATTENTION: All designers and researchers. Use these AI tools to supercharge your toolkits.
What Are UX AI Tools?
UX AI Tools are digital platforms that use artificial intelligence to aid in product development.
Product designers can implement these applications throughout the research and design process.
Use UX AI tools to help manage all design activities. Generate new content and ideas when beginning a project. Designers use AI-powered UX software to create wireframes or prototypes for user testing. AI can collect, process and analyze large swathes of research data much faster than a human. After testing prototypes with users, AI UX Tools provide suggestions to improve the product experience and flow.
Implementing AI UX Tools increases the productivity and scale of design. Analyzing more data from a wider range of stakeholders allows researchers to conduct deeper analysis. Leveraging AI can greatly enhance the creativity of a company’s design practice. They facilitate collaboration across an organization, creating a user-centric culture.
AI UX Tools help designers create more intuitive and user-friendly designs.

The Pros and Cons of AI in UX
AI promises to have a big impact on a UX teams:
- Productivity & Efficiency – Designers and researchers can automate mundane tasks to improve productivity. Automation saves time and human effort. This accelerates a product’s development time.
- Financial Standing – Outsourcing certain tasks to AI reduces designer and developer costs. This impacts overall profitability.
- Creativity & Agility – AI’s ability to endlessly churn output allows designers to generate several new design concepts. Overcome design bottlenecks with AI.
Let’s further examine the benefits and limitations of implementing AI in the UX process.
Benefits of Using AI in the UX Process
Traditional research methodology involves manual and tedious work. It’s slow — taking up a huge chunk of a researcher’s time. Not anymore, thanks to AI.
The benefits of using AI in the UX process are aplenty:
- Workflow Automation. AI automates repetitive and mundane tasks such as scheduling interviews and sending notifications. It can also conduct more advanced tasks such as user testing and data analysis, allowing researchers and designers to focus on more strategic work.
- Automated Data Collection. Collate data from multiple sources such as social media websites, website analytics, surveys, focus groups and usability testing. Tools can categorize and organize data without the need for human intervention.
- Real-time Data Analysis & Insights. Analyze large datasets faster with pattern recognition and anomaly detection. AI uncovers trends, patterns and insights missed by humans. It also analyzes data faster and more accurately than humans. This allows for a deeper understanding of user habits, preferences and needs.
- Reduce Human Bias & Error. Manual transcription and traditional analysis gives rise to human error. AI mitigates this by removing human involvement until it’s necessary.
- Personalization. Companies continuously observe and record user behavior. AI algorithms can handle large volumes of this user data. AI provides customized recommendations tailored to various users After analyzing people’s preferences. With AI, interfaces feel tailor made for each individual.
- Predictive Capabilities. AI can build predictive models that humans simply can’t. Algorithms anticipate user behavior and preferences with high accuracy. This opens the door for more intuitive interfaces and seamless experiences.
- Content Generation. Generative AI tools can help designers quickly create prototypes and wireframes. Options can be customized to different user groups. AI tools also offer writing assistance in creating audience-specific copy for product content.
Limitations of AI Design & Research Tools
Leveraging the full potential of AI requires a deep understanding of its inner workings. How does it utilize data and impact users’ lives? As with any technology, it’s important to understand AI’s constraints:
- Context – AI can’t understand how output feeds into study goals or research questions. AI has no background information about the product or users, and it doesn’t lean on insights from previous research. Systems don’t know what factors are most important to the researcher. They can’t ask pointed questions and alter the course of interviews.
- Loss of Human Touch – AI lacks basic awareness of human psychology. It doesn’t have human empathy, creativity and emotion. For instance, in logo design: AI may be able to suggest color palettes. What it CANNOT do is capture the subtleties of human emotion – the type of reaction it evokes in users.
- Ethical Considerations – All AI tools are trained on biased datasets (systematic bias). Any tools that claim otherwise are just plain wrong. Using a non-representative dataset introduces statistical biases. AI doesn’t discriminate and uses biased input if provided with it. It falls on the researcher to take this into consideration and produce bias-free insights.
- Noisy data – AI algorithms are constantly referred to as a ‘black box’ – we might never know their inner workings. Some tools generate content without attributing the source of the information. A lack of citation means that AI output can’t be validated. Furthermore, it can be influenced by questionable sources (plenty of those out there!) and throw out inaccurate output. It also can give you two different answers for the same question – there’s no consistency. A lack of transparency around the process introduces the element of doubt in AI output. Validate AI powered output before using it in analysis.
AI will always need humans to corroborate results. Researchers and designers must ensure that AI has carried out its task correctly and fairly. Humans will always be responsible for final decision-making.
For a deeper dive, here’s more on the merits and demerits of AI in UX.
AI and the UX Design Process
AI can lend UX professionals a helping hand during different phases of the design process. Identify pain points or areas that need improvement in your existing workflow. Use these questions understand more about where you can integrate AI:
- What are my current roadblocks?
- What tasks need optimization?
- What’s the expected outcome?
Check out our guide on how to use AI every stage of the UX process.
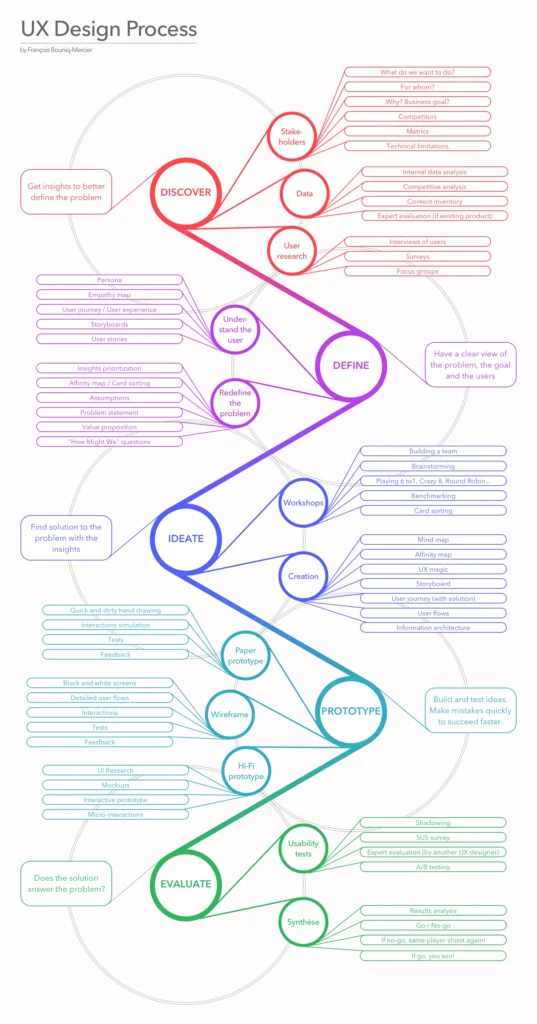
Designer Francois Bouniq-Mercier created this stunning visualization of the design process.
This gorgeous graphic showcases a classic UX design process based on design thinking principles. (As we continue, you’ll notice we’ve used it to identify the stages ripe for AI use.)
Researchers at Linköping University in Sweden investigated how to augment UX research and design with AI. They interviewed several UX professionals to find out how they were incorporating AI into their workflow.
Participants used generative AI tools like Midjourney, ChatGPT and Dall-E.
Some queried the tools, looking for inspiration as they began the creative process. Others used it for benchmarking, editing color palettes and changing UI elements.
A general consensus among interviewees was AI will increasingly become part of their workflow. Output they received was of high quality and required very minor manual changes. Tools like Midjourney allow designers who aren’t experts in 3-D modeling to quickly iterate on designs. AI may even start to make design recommendations after reviewing final prototypes and user behavior.
It’s all about finding an AI tool that complements your existing processes.
Choosing the Right AI Tools for UX
Since all the hype surrounding AI from ChatGPT’s release, companies are racing to roll out new AI functionality. Be wary of tools slapping on “AI” in their marketing just for kicks (and clicks).
Features and functionality aside, consider these important factors when comparing AI tools:
- Costs
- Scalability
- User Friendliness
- Integrations
Don’t forget to pay heed to these important considerations before diving into a comparative analysis of the tools out there:
- Business Goals. What business objectives does the project help satisfy?
- Project Needs. Whether it’s a survey, user testing or data analysis – what does the project (and regular projects) require?
- Features and Compatibility. What features do you need for this and future projects? (More in the section below)
- Training & Support. What training resources and support does the company provide to ensure effective adoption and use of the tool?
- Scalability & Flexibility. Will the tool be able to satisfy not only current needs, but future ones as well? UX Tools must adapt to evolving project needs and growing needs of the UX research process.
- Secondary Benefits. Look out for versatile AI tools with features that support other areas of the UX process. For example, Marvin acts as an AI research assistant, facilitating data collection and analysis in one place. It also seamlessly integrates with all your existing tools. Two birds with one stone. That’s Marvin.
- Data Privacy Compliance. What regional and international regulations must be adhered to?
Privacy Concerns
Companies constantly recruit participants and users for interviews, focus groups and surveys. It’s their duty to protect user data at all costs. Concealing people’s personally identifiable information (PII) is of utmost importance.
Choose a tool that incorporates these data security measures:
- Data Anonymization – remove PII from any collected or stored data
- Data Encryption – prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information
- Compliance – ensure tools abide by regulations. These include local data protection laws, industry norms and ethical guidelines.
- Limited Data Collection – minimize unnecessary data collection. Focus on collecting what matters.
- User Consent – choose tools that are transparent with their data usage and security.
Marvin uses advanced privacy filters to blur faces and scrub out any PII from interviews recordings. It’s HIPAA, GDPR and SOC2 compliant, so your user data is always protected.

How to Choose AI Tools to Augment UX Workflows
Choosing from the ever-expanding universe of AI UX Tools can be daunting. Where do you even begin?
In the section above, we focused on what to look out for when comparing tools. Before diving in headfirst, it’s essential to first identify what stage of the design process could use some AI assistance.
Take stock of your current processes to identify weaknesses or inefficiencies. Then use our list below to explore how AI can help rectify them.
Phase I – Discover
Stay up-to-date with the market. Look for tools with data analysis capabilities. Algorithms analyze large and complex datasets accurately and help uncover insights rapidly. Conduct a competitive analysis. Market research tools can scrape and analyze data from competitor websites, social media and customer reviews to identify patterns and industry trends.
Tools can even catch insights that might’ve ordinarily been missed. They also carry out data analysis tasks in a fraction of the time.
Tools: IBM Watson Discovery, Google Trends, SEMRush, Research AI, Qualtrics, Marvin
Phase II – Define
Researchers or designers could use some help. Let AI tools become your new virtual assistant. Software can now transcribe user interviews as you conduct them, freeing up a designers mindspace for the questions ahead. From summarizing long transcripts to creating notes and synthesizing insights, let your research assistant conduct preliminary analysis for you.
Tools for Research and Design Assistance: Adobe Sensei, GitHub Copilot, UX Pilot, Stable Diffusion, Marvin
Plus, all that data needs a place to live. Learn more about the universe of research repositories.
Phase III – Ideate
Brainstorm ideas and concepts using content generation tools. Create user journey narratives and maps to understand more about their experiences. Tools use sentiment analysis to analyze social media, forums and feedback to craft detailed user personas.
Tools: ChatGPT, Blush, Canva, InVideo, TheyDo, QoQo
Use generative AI tools for UX & Product Writing. Populate wireframes with audience specific copy that’s optimized for search engines and different user personas.
Tools for UX Writing: Writer, Copy.ai, Jasper, Content Bot, Grammarly
Phase IV – Prototype
Automate design workflows. AI tools can generate Ul layouts from user requirements and design principles. Generate interactive and realistic wireframes in minutes with prototyping tools. Simply write a prompt and let the tool create several options for you to choose from. Designers can test and iterate on designs much faster with a shorter feedback loop. Save time and effort with these tools.
Tools for Prototyping: Uizard, InVision Studio, Ando, Midjourney, Framer, Fronty, Visily, Botpress, Prott, Mockplus, Galileo AI, Relume
The above products create wireframes that serve as a foundation for design. You can then edit and tweak elements according to your liking. Tools offer color palette matching, font suggestions and provide access to a large library of icons and logos. They even provide recommendations, helping designers in making informed choices.
Use AI to create stunning user interfaces. To enhance your UI and branding with AI, use the following:
Tools for UI Elements & Branding: Adobe Sensei, Figma, Canva, Fontjoy, Designhill Al Logo Maker, Khroma, Recraft AI, Sketch2React, Coolors, Colormind, Flair AI, Magician Design, Dall-E 2, Marvel AI
Phase IV – Evaluate
User research and behavioral analysis tools track usage patterns. They use heatmaps, eye tracking, session recordings, surveys and A/B tests to understand how users interact with Ul designs. Some tools offer predictive insights, using historical data combined with Al training data to simulate user behavior or responses.
Tools that offer user testing automation can expedite different aspects of testing such as sentiment analysis and usability testing. Some tools include AI-powered tools such as card sorting, tree testing and first click testing. These tests provide valuable insight into the user preferences and inform the design process moving forward.
AI tools can also help with design flaw detection. They provide instant feedback on design choices, potential usability issues and accessibility considerations.
Tools for Usability Testing: Maze, Visualeyes, Brainpool, Optimizely, Dscout, UserTesting, Lookback, Hotjar, Attention Insight
List of Top 8 UX AI Tools to Consider
We scoured the web to bring you the top 8 AI UX tools that enhance a designer’s or researcher’s workflow. Each AI tool falls under the stage of the design process it augments.
Discovery Phase
1. Marvin
Marvin brings companies’ disparate data into one centralized repository. This makes it easier than ever to collect, organize, analyze and share insights. AI-powered smart workflows let people search across data and find answers in minutes.
Designers can go as deep or as high-level as they want, while making connections across data sources they would’ve otherwise missed. Marvin’s AI note taker is the first of its kind, and it automatically generates notes from lengthy interviews. This provides a foundation for researchers to build on as they delve deeper into analysis.
The best part? Marvin integrates seamlessly with applications designers already know and love. Don’t uproot your workflow to accommodate new AI UX Tools — find a product that layers on top of your process and makes it easier to do your job.
All your research in one place. That’s Marvin.
2. Qualtrics
Experience management platform that focuses on customer and employee experience and strategic research.
Qualtrics is an online tool that enables designers to build, distribute and analyze surveys. This software has powerful AI capabilities besides collecting and processing quantitative data. Algorithms analyze vast amounts of data from chat logs, social media feeds, feedback surveys. They use all this data to generate insights. The AI engine recommends actionable next steps in order to drive tangible business outcomes.
Definition Phase
3. QoQo
A ‘UX design companion’ that’s powered by OpenAI (same as ChatGPT). QoQo helps you generate well-rounded user personas from scratch. It builds cards representing each user’s goals, needs, motivations, frustrations and tasks. Map the user journey or get assistance with design briefs and information architecture. QoQo has a Figma plugin, so you can leverage its AI while designing.
It’s important to use QoQo in conjunction with your own user research. It serves as a great AI companion and starting point for user research.
Notable Mentions: NotionAI. Helpful for organizing design ideas and creating documentation for when you begin a project.
Ideation Phase
4. ChatGPT
If you haven’t already heard of ChatGPT, chances are you’re living under a rock. We like to think of it as a design assistant or intern.
ChatGPT uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) to generate content based on text prompts. Use ChatGPT to outline research plans, create product documentation and user guides. Brainstorm and frame interview questions and generate compelling written copy for your UI. ChatGPT serves as a constant idea generator that can spark creativity among designers. It enables designers to automate mundane tasks and streamline their workflow.
Notable Mentions: Midjourney. Create designs from ideas in minutes using this text-to-image generation tool.
Prototype Phase
5. Uizard
Unanimously the number one choice amongst all prototyping apps. Uizard uses AI to generate wireframes from written prompts. Create prototypes by dragging and dropping UI elements into a design. You can even hand draw a sketch, and Uizard will convert your design into an editable mockup. It even generates code from the sketch to boot.
Use Uizard to iterate endlessly. It creates prototypes based on design best practices. Create aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly designs.
6. Adobe Sensei
Adobe’s suite of applications including Photoshop, Illustrator and InDesign all house Sensei.
It has numerous AI features and functionality that help automates non-creative tasks. Content-aware fill allows you to quickly replace unwanted objects from an image. Smart object selection enables users to make complex selections with a simple click and drag. Sensei even acts as a design collaborator. Use it to generate alternate layouts or suggest font and color pairings for any design.
Evaluation Phase
7. UserTesting
A one-stop customer experience platform that helps researchers understand their target users. Recruit and onboard study participants on UserTesting. Using AI, conduct a sentiment analysis on large volumes of text extracted from audio, video and other file formats. ML algorithms conduct keyword mapping, by grouping sentiments based on certain words.
UserTesting’s AI helps identify points of friction in user interactions. Collating data from multiple sessions allows you to visualize the user journey. It generates themes from large volumes of data so you can begin with some preliminary analysis already in place.
8. Attention Insight
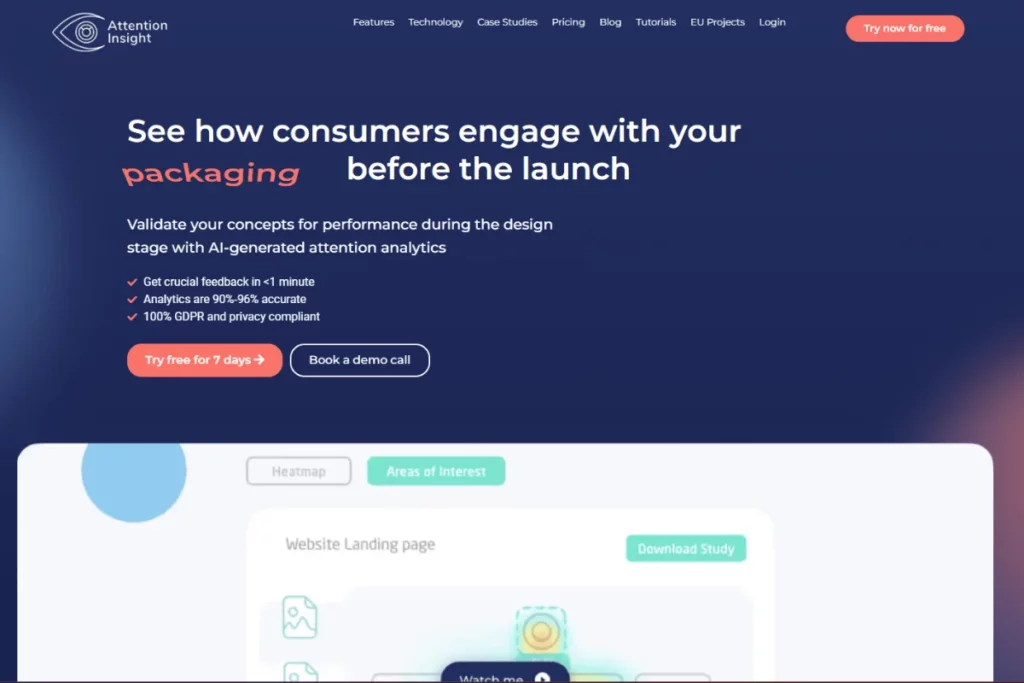
An AI powered tool that provides design analytics. Attention Insight simulates eye-tracking studies and preference tests. Heatmaps and focus maps help identify elements that grab the user’s attention as they navigate through a website or application.
These insights help uncover usability issues or potential roadblocks in the user interface. Equipped with this information, you can make more informed design decisions. Improve usability, optimize product performance and create more user-centric designs. Track and monitor how product updates enhance conversion rates.
Notable Mentions: VisualEyes. Powered by AI, this application performs similar tasks to Attention Insight.
Best Practices for Integrating AI into UX Workflows
Below are some steps on how to best to incorporate AI into your work:
- Soft Launch – Start Small. Run tests on a smaller, manageable project to test AI’s handling of data. This allows you to identify and iron out any kinks or inefficiencies. Before releasing it across the entire organization, roll out AI tools on a limited scale. This enables an understanding of whether people are receptive to, and will likely adopt the technology. Here are some ideas about scaling research and design operations.
- Data Quality Assurance – Remember, your output is only as good as your input. (We know you’ve heard it before: Bad data in, bad data out.) Focus on good data quality to ensure you’re using datasets that are accurate, complete and consistent. Unbiased and reliable data generates helpful and actionable insights. Set explicit data validation guidelines for data collection to avoid errors and anomalies in the future. Address the quality of your data, don’t neglect it.
- Ensure Human Oversight – Keep user experience in mind throughout the process. Sounds simple enough, but it’s easy to become enamored by the capacity of AI. Researchers and designers can lose sight of who they’re designing for. Don’t fall into the trap. Ensure a varied group of individuals review and test the system before launch.
- Validate Regularly – Don’t rely solely on AI’s output. Cross-check AI’s findings with human analysis to corroborate insights accurately.
- Consider Ethical Implications – FACT: AI is trained on biased data. It’s a designer’s duty to ensure that any inherent biases don’t exist in design output. Clearly define the scope of AI used in any project and use it responsibly. Google’s Rida Qadri weighs in on the ethical dilemma facing researchers today.
- Familiarization – Companies are rolling out new AI capabilities at a rate of knots. Stay up-to-date with the latest trends and future developments in the field. Prioritize continuous learning. We share our thoughts on how to master user research software.
- Training – Establish best practices for employees at the company to follow. Learning the tool’s functionalities is important, but don’t forget to teach users how to interpret and use AI generated outputs. Educate them on how AI could fit into their workflow. Once they learn the ropes, they can offer feedback for improvements. (Marvin customers do this all the time, and we LOVE them for it!)
- Iterative Methodology – Iterate your work using AI to meet functional and aesthetic needs. Don’t merely accept the first round of AI generated assets. Keep refining the process until it meets your requirements. Create a feedback loop – test wireframes to get quick user feedback and observe where they fall short. If you don’t like something about a certain wireframe, change it. This creates well balanced and effective designs.
- Collaborate – Constantly communicate with stakeholders, developers and end users. Involve them early in the process. Establish a shared understanding of business goals, the potential benefits and constraints of AI tools. Marrying diverse perspectives and user needs with project objectives leads to a more impactful user experience. Don’t believe us? Learn why industry expert Lou Rosenfeld thinks research can eliminate organizational silos.
AI and UX: Better Together
AI’s impact on the user experience can’t be understated. We’re only at the beginning of the story. The rate at which AI tools are being rolled out is staggering. AI will only become larger in terms of its significance and reach.
Design’s mandate doesn’t waiver — let’s create experiences that delight users.
AI will increasingly help us on this path.
Using AI, experiences can be customized to individual needs and abilities. UX professionals can extract meaningful customer insights from feedback at scale. This improves functionality and aesthetics of the final product or service. It forms intuitive and engaging customer journeys.
AI empowers designers to create engaging products with greater purpose. Unlock greater productivity with AI.
Blog hero image by Pete Wright on Unsplash

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Now, let’s look at the top FAQs about UX AI tools.
How Do AI Tools Improve User Testing and Data Collection?
UX AI Tools can assimilate large volumes of data from various sources. By automating data collection and processing, a company benefits from efficient data management. Machines analyze data at scale to gauge user behavior and sentiment. AI-enabled analysis doesn’t suffer from design bias and human error.
AI streamlines aspects of user testing. To optimize resource spend, designers can automate aspects of the testing process. UX AI tools can identify potential bottlenecks and usability issues. They can also make suggestions to increase a design’s accessibility. This helps in optimizing design for the prototype stage. A continuous feedback loop facilitates faster product development.
Using AI tools, designers enhance the user experience of a product. It results in them creating more intuitive, personalized and inclusive designs.
Can AI Tools Predict User Behavior in UX Research?
Yes, absolutely!
UX AI tools use Machine Learning (ML) algorithms to collate and analyze historical data. Algorithms learn from terabytes of datasets to unearth trends and patterns. They use past data to make predictions about future trends and user behavior.
Advanced algorithms track user behavior and sentiment. They detect patterns in data that help designers create well defined user personas. Designers can customize user journeys based on these personas that AI helped create.
Predictive analytics helps in forecasting user behavior patterns. ML algorithms continuously learn from data. This increases the precision of their predictive abilities over time.
Predictive analytics helps designers identify navigation weaknesses in the user flow. This helps designers adapt the interface for more user-centric design. Designers can make anticipatory changes and feature improvements to create a smoother UI.
How Do AI Tools Handle Qualitative Data in UX Research?
UX researchers conduct user interviews to obtain qualitative data. They gather user testing feedback and ask open-ended questions to do so. Participant responses are often lengthy and complex.
UX AI Tools like Marvin can automatically generate transcripts from interview clips (both audio and video). They store this data in a research repository.
Once stored, this data must be analyzed. AI tools aggregate thousands of hours of user interviews, to identify common themes. To gauge user delight or frustration, they scan interview transcripts to conduct a sentiment analysis. This serves as a foundational, preliminary analysis before any human intervention.
AI tools can process large amounts of qualitative data at inhuman speeds. They summarize multiple pages documents within minutes.
AI tools expedite the time consuming and tedious aspects of handling qualitative data.